MX Records
What are MX Records?
MX is an abbreviation for 'Mail Exchanger'. MX Record or Mail eXchanger record refers to the public DNS records of the domain, which indicate where the emails pertaining to the recipient domain (essential part of the email address) should be routed to. It is configured in the DNS (Domain Name System).
Generally MX records translate an IP address of an email server or Mail Transfer Agent (MTA), which can receive emails. It signals where an email should be routed on the Internet.
What is the purpose of an MX record?
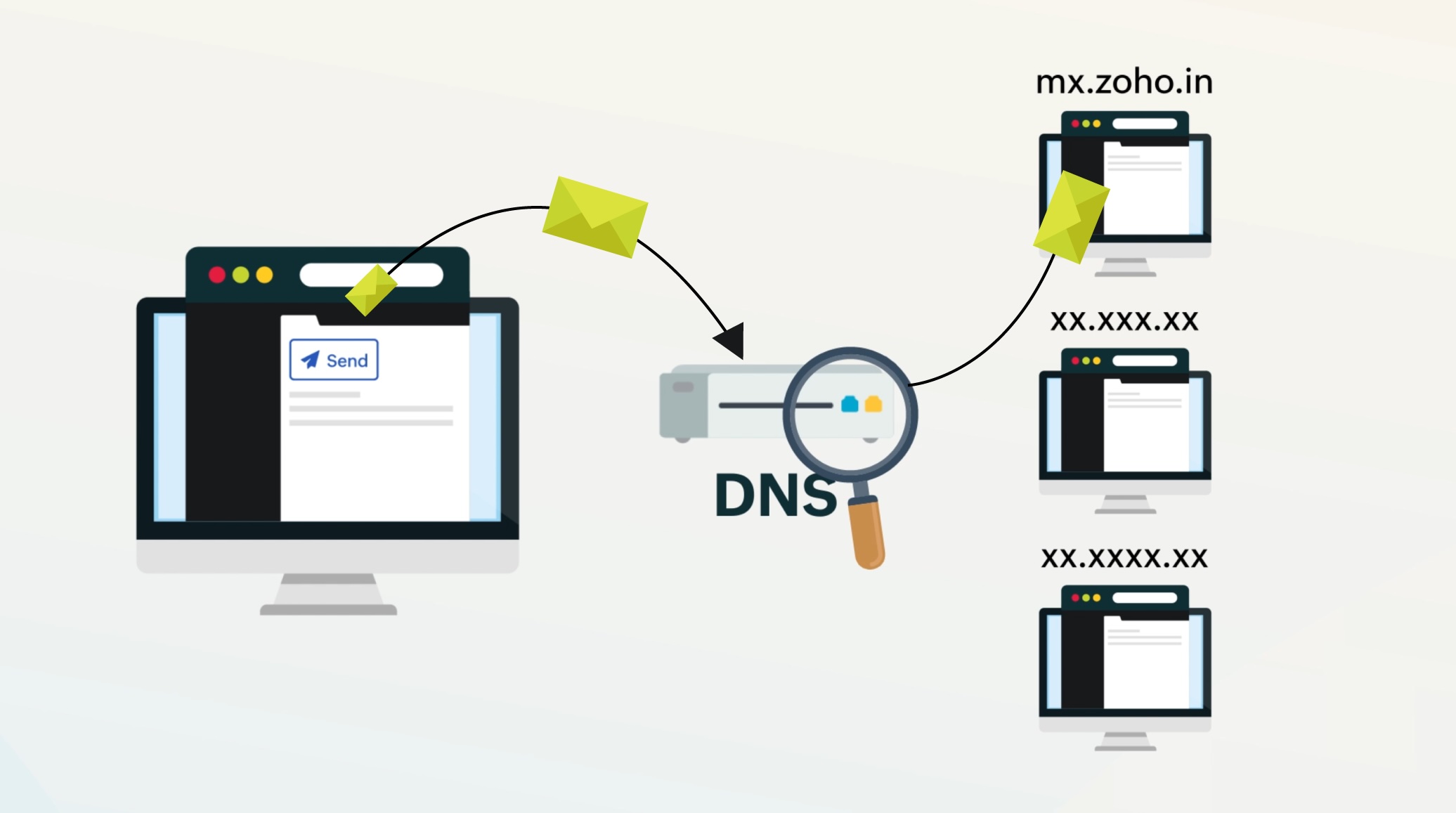
An MX record points to a mail server that accepts incoming emails for a domain. It is a resource record in the DNS that indicates where an email will be delivered in compliance with the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
Examples of MX Records
| Domain/ Subdomain | Record Type | Priority | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| @ | MX | 10 | mx.yourprovider.com |
| @ | MX | 20 | mx2.yourprovider.com |
Priority in MX Records
The MX records of a domain have a parameter called priority.
A particular email server can receive the emails of multiple domains, and can also experience overload. To load balance and avoid outages, the email providers support multiple servers, with different MX records. These are differentiated by the priority number in the MX Records. Emails get delivered to the MX record with the lowest priority number. To load balance and avoid outages, users can add multiple servers to an MX record and select a priority order. Mail is sent to the MX record with the lowest priority, or evenly across multiple servers if they have the same priority.
In the above example if the email server associated with mx.yourprovider.com experiences an overload, the emails get routed through the email server 2, namely mx2.yourprovider.com.
What is MX Lookup?
MX Lookup is the process of looking up the MX record of the domain. When you send an email, your email reaches your sending server's Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) - component responsible for the transferring emails - sends a DNS query to the recipient domain to identify the email server to which the email should be transferred to. The sending MTA establishes an SMTP connection with the identified email server and transfers the email to the recipient server. The recipient server then relays that email to the corresponding mailbox hosted in the server.
Can MX records point to a CNAME?
Generally a CNAME record is used to refer a domain's alias instead of its actual name. CNAME records in turn point to an A record (IPv4) or AAAA record (IPv6) for that domain. However MX records may point directly to another A record or AAAA record, which are valid mail servers. As per RFC that define MX records, MX pointing to a CNAME is forbidden.
How does an MX record work?
When an email is sent to example@company.com the following events take place:
- When you send an email, the email client you use, sends the email to the sending server, or your email provider's server.
- Your email provider looks up and picks all the recipient email addresses added your email.
- For each recipient email address, the sending server checks the domain names.
- The sending server does an MX Lookup from the DNS of the recipient domain.
- These MX records along with the priority tell sending servers where to route emails for a domain.
- The emails are then delivered to the recipient email server, based on the result of the MX Lookup.
- The steps 4 to 7 are repeated for each recipient email domain, picked from recipient list in your email.
If the server with the lowest preference is unable to accept emails at a particular time, then the email will be delivered to the server with the next highest priority. You can look up your MX records to know your MX details such as the IP, priority etc. You can also lookup other DNS records using a DNS checker tool.